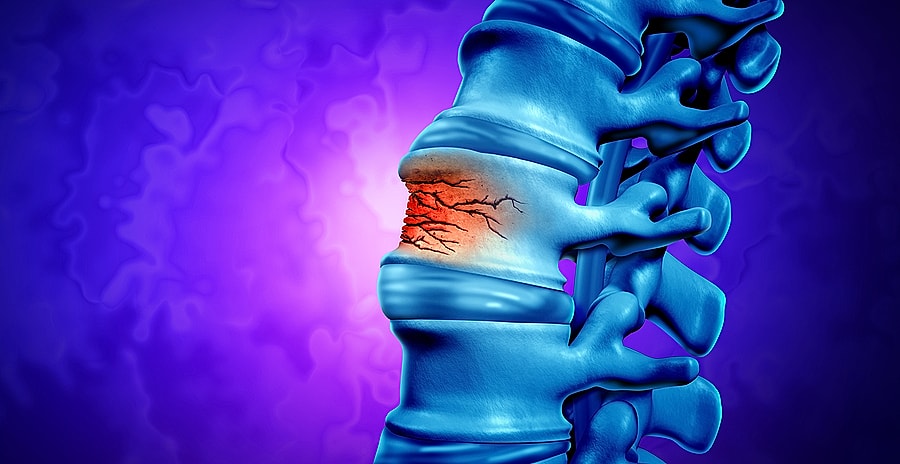
The long term effects of spinal compression fractures can be far-reaching, potentially leading to prolonged discomfort, permanent changes in posture, and even a decreased quality of life. Understanding these long-term impacts is crucial, as it underscores the importance of timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventative care.
One of the most common long term effects of spinal compression fractures is severe back pain. This pain can occur suddenly or gradually over time and may be localized to the affected vertebrae or radiate throughout the back. The pain may worsen when standing, walking, or twisting and may improve when lying down.
Compression fractures can cause the spine to lose height, resulting in a shorter stature. This may be accompanied by a visible hump in the upper back, known as a dowager's hump. This condition can lead to a decrease in self-esteem and confidence.
Another long term effect of spinal compression fractures is limited mobility, making it difficult to bend, twist, or move in certain ways. This can have a significant impact on daily activities and quality of life. Limited mobility can also lead to weight gain, which can further exacerbate the symptoms of spinal compression fractures.
If a compression fracture compresses a nerve in the spine, it can lead to numbness or tingling in the arms, legs, or torso. This may also be accompanied by weakness or difficulty with coordination.
One of the most common causes of spinal compression fractures is osteoporosis, a condition in which the bones become brittle and fragile. According to the National Osteoporosis Foundation, approximately two million fractures occur each year due to osteoporosis. Long term effects of spinal compression fractures from osteoporosis are more common in women and older adults.
Compression fractures can also be caused by trauma, such as a car accident or fall. These types of fractures are more common in younger individuals or those with healthy bones. Trauma-related spinal compression fractures may occur in athletes or individuals who engage in high-impact sports.
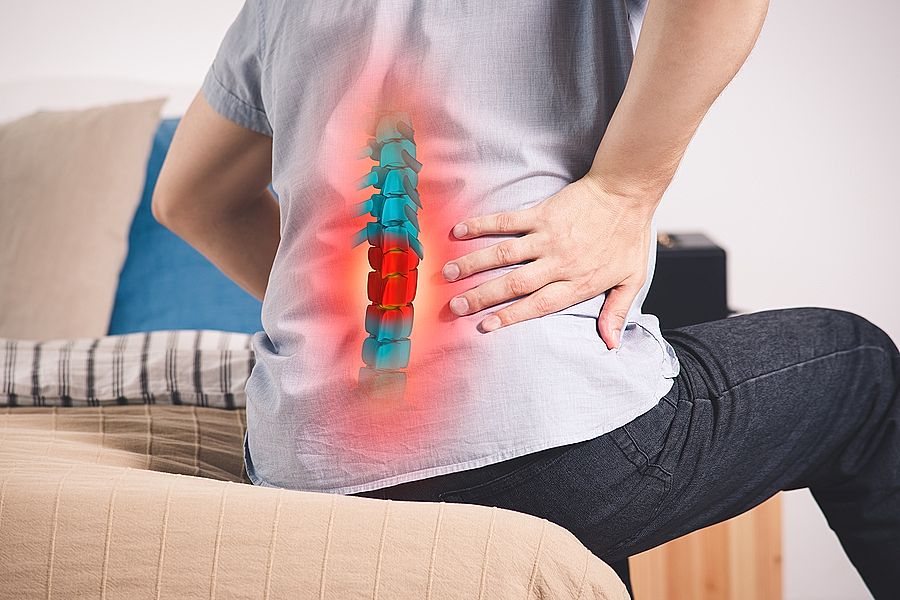
In many cases, conservative treatments can be effective in managing symptoms of spinal compression fractures. These may include rest, pain medication, and physical therapy to improve mobility and strength. Conservative treatments are typically recommended for mild to moderate spinal compression fractures.
For more severe cases, minimally invasive procedures may be recommended, such as kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty. These procedures involve injecting a cement-like material into the fractured vertebrae to stabilize it and reduce pain.
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a spinal compression fracture. This may involve fusing the affected vertebrae together or removing part of the bone. Surgery is typically reserved for severe spinal compression fractures that have not responded to conservative or minimally invasive treatments.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can help to reduce the risk of osteoporosis-related spinal compression fractures. Foods rich in calcium and vitamin D are also important to help mitigate the long term effects of spinal compression fractures.
Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, running, or weightlifting can help to improve bone density and reduce the risk of spinal compression fractures. Low-impact exercises such as yoga and swimming can also be beneficial for improving mobility and flexibility.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to bone loss and increase the risk of spinal compression fractures. By avoiding these habits, individuals can reduce their risk of developing osteoporosis and other conditions that can lead to spinal compression fractures.
Activities such as high-impact sports, heavy lifting, and manual labor can increase the risk of spinal compression fractures. By using caution and taking appropriate safety measures, individuals can reduce their risk of injury and spinal compression fractures.

At The Institute for Comprehensive Spine Care, I specialize in the treatment of spinal fractures and am deeply committed to providing personalized care that addresses your unique needs and goals.
With more than 20 years of experience treating various spinal conditions, my team and I offer the latest advancements in preventive care and minimally invasive surgeries. I prioritize clear communication and personalized attention for each of my patients, ensuring that you receive expert care every step of the way. I firmly believe that the best care starts with patient education and a customized approach to treatment, and my team and I are dedicated to supporting and guiding you through your journey to recovery.
Don't let the long term effects of spinal compression fracture hold you back any longer. I invite you to schedule a consultation today and discover how I can help you reduce pain, increase mobility, and improve your quality of life.